Git 這個工具的分支處理基本上依靠 merge 和 rebase 來實現,然而這兩個指令加上 flags 可以組成十幾種不同的結果,情況可以變得很複雜,大部分的人(包括我)都不敢說了解他們之間的差異,以及他們的應用場景。下面就讓我帶大家分析。
git merge
合併兩個分支的變更。如果可能,Git 會進行一個快進合併(fast-forward merge),即直接將目標分支指針移動到源分支的最新提交。
示意圖
1A-----B---C feature2 /3D---E---F---G main使用 git checkout main 然後 git merge feature:
1A-----B-------C feature2 / \3D---E---F---G---H maingit merge --squash
將一個分支的所有提交壓縮成一個單獨的提交(但不保留分支的提交歷史),再合併到當前分支。
示意圖
1A-----B---C feature2 /3D---E---F---G main使用 git checkout main 然後 git merge --squash feature,接著 git commit:
1A-----B---C feature2 /3D---E---F---G---H main其中,H 是一個新的提交,包含了 B-C 的所有變更,但不保留這些提交的歷史。
git merge --no-ff
強制執行一次非快進合併,即使能夠進行快進合併也會創建一個新的合併提交。
示意圖
1A---B---C feature2 \3 D---E main使用 git merge --no-ff feature 後:
1A---B-------C feature2 \ \3 D---E---F mainF 是一個新的合併提交,即使合併可以快進,還是會產生合併紀錄。
git merge --no-commit
執行合併但在自動提交前暫停,允許用戶檢查或修改合併結果。
示意圖
同 git merge,但在合併後不會直接創建合併提交 H,允許手動檢查和提交。
git merge -e
與普通的 git merge 類似,但在創建合併提交前,可以編輯提交信息。
git rebase
將一個分支上的提交重新應用於另一個分支的頂部。
示意圖
1 A---B---C feature2 /3D---E---F---G main執行 git checkout feature 然後 git rebase main:
1 A'---B'---C' feature2 /3D---E---F---G mainA'-B'-C' 是重新播放的提交。
註: 上面的執行步驟等價指令: git rebase main feature。
git rebase -i
以交互式方式重新應用提交,允許修改、刪除或合併提交。
示意圖
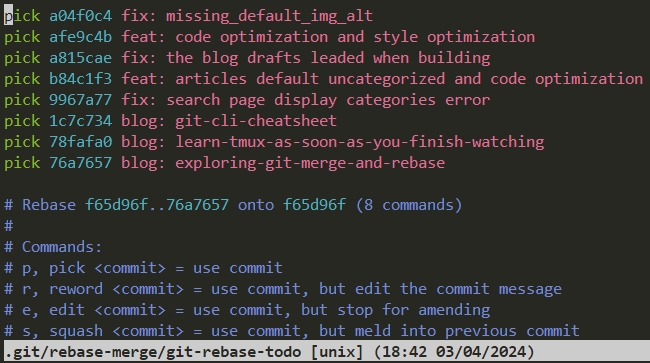 git cl 的介面 (越下方的提交越新)
git cl 的介面 (越下方的提交越新)
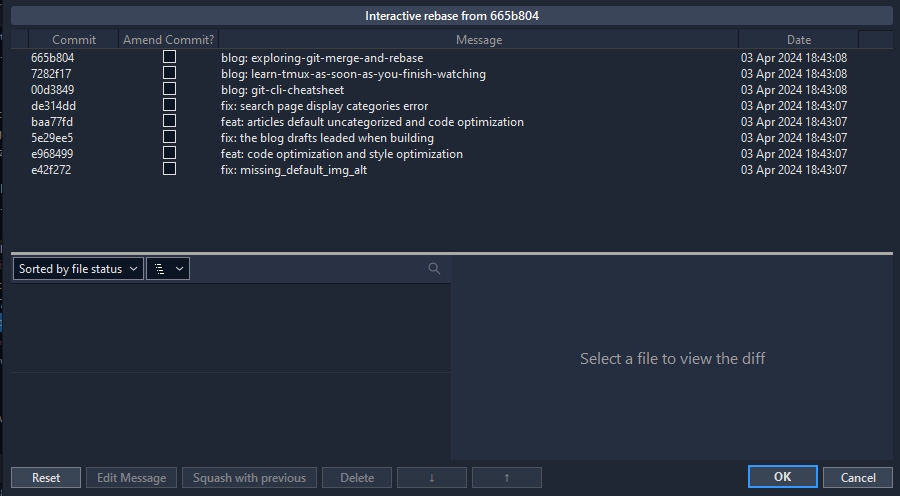 sourcetree 的介面
sourcetree 的介面
git rebase --onto
將一個分支上的一些提交重新應用到一個不同的基底上。
示意圖
因為太經典了,容我擷取 Git - git-rebase Document 的示範:
Here is how you would transplant a topic branch based on one branch to another, to pretend that you forked the topic branch from the latter branch, using rebase --onto.
First let’s assume your topic is based on branch next. For example, a feature developed in topic depends on some functionality which is found in next.
1o---o---o---o---o master2 \3 o---o---o---o---o next4 \5 o---o---o topicWe want to make topic forked from branch master; for example, because the functionality on which topic depends was merged into the more stable master branch. We want our tree to look like this:
1o---o---o---o---o master2 | \3 | o'--o'--o' topic4 \5 o---o---o---o---o nextWe can get this using the following command:
1git rebase --onto master next topicAnother example of --onto option is to rebase part of a branch. If we have the following situation:
1 H---I---J topicB2 /3 E---F---G topicA4 /5A---B---C---D masterthen the command
1git rebase --onto master topicA topicBwould result in:
1 H'--I'--J' topicB2 /3 | E---F---G topicA4 |/5A---B---C---D masterThis is useful when topicB does not depend on topicA.
A range of commits could also be removed with rebase. If we have the following situation:
1E---F---G---H---I---J topicAthen the command
1git rebase --onto topicA~5 topicA~3 topicAwould result in the removal of commits F and G:
1E---H'---I'---J' topicAThis is useful if F and G were flawed in some way, or should not be part of topicA. Note that the argument to --onto and the <upstream> parameter can be any valid commit-ish.
git pull --rebase
從遠程倉庫更新當前分支,並將本地的更改重新應用在拉取的更新之上。
示意圖:
1 A---B---C main (local)2 /3D---E---F---G main (remote)使用 git pull --rebase 後:
1D---E---F---G---A'---B'---C' main (local)